Understanding Computer Vision
Computer Vision (CV) is an important field of Artificial Intelligence (AI), enabling machines to understand and interpret the vast amount of visual information in our physical world. Like how people use their eyes and brains to identify objects, movements, and scenes, CV enables machines to process images and video to make decisions based on what they “see.”
The possibilities created by this technology allow for computers to visually identify faces, detect objects, follow movement, and understand complex visual environments. CV uses a combination of algorithms, Machine Learning models, and large datasets to take raw data captured by cameras and turn it into actionable insights that support business and other applications. As the application of AI continues to grow, so will the capabilities of CV, making it easier for businesses and organizations to leverage automation, safety, and innovation across areas such as Healthcare, Automotive, Security, Manufacturing, Entertainment, and many others.
The Basics of Computer Vision
Computer Vision uses computational methods to enable machines to recognize objects in images and videos, much as we do with our eyes. First, computer vision captures video and still images using camera and/or sensor technology. Once captured, it must be processed using mathematical and computational methods to define shapes, colors, textures, and relationships.
The most important component of computer vision is the algorithm(s) used to extract features from an image (e.g., edges, textures, and object boundaries). Computer vision relies heavily upon machine learning to allow computers to “learn” from large databases of labeled images. As the computer learns, its ability to accurately recognize and adapt improves. There are many examples of computer vision being utilized today in all industries, including but not limited to: Healthcare – Medical Image Analysis; Automotive – Lane and Obstacle Detection; Security – Facial Recognition/Motion Detection; Entertainment – Augmented Reality/Visual Effects.
Definition and Importance
Defining terms for complex technologies, such as computer vision, is necessary. A common understanding of what the term means will help eliminate misunderstandings and enable productive conversations. Defining computer vision clearly shows how the field acts as a connection between visual information and smart decisions.
It is very important to understand computer vision because it is at the heart of many current technological advancements, which provide better user experiences, increase safety, and enhance efficiency. The rapid growth in the volume of visual data is making it increasingly important to have accurate systems to process it.
Everyday Applications in Technology
Visual intelligence (computer vision) has become a common part of people’s day-to-day lives. With smartphones, we can use computer vision to unlock our phones with our faces, organize photos, and enhance the quality of our smartphone cameras. We also use it in navigation apps that can create maps from visual data, as well as to analyze traffic patterns. Online platforms are also using vision systems to assist with monitoring their content and conducting searches based on image content.
Retailers have used computer vision through self-service checkout systems and real-time inventory tracking. Banks have used computer vision to help verify identities when processing online transactions. In education and entertainment, computer vision is used to make learning more fun and engaging for students through interactive, immersive visuals. All of these examples illustrate how visual intelligence can make many tasks easier and more convenient.
The Role of AI in Vision
AI has greatly improved computers’ ability to comprehend and process visual data. Prior to the emergence of AI, images were processed using predefined algorithms. Now with AI, machines can continue to learn from experience and adjust their behavior in response to that learning.
AI is being used in medical settings to help doctors interpret X-rays and MRIs by allowing them to use an AI-powered vision system. Additionally, AI is used in self-driving cars to interpret real-time visual information and make decisions about steering and braking. Furthermore, AI is also used for facial recognition and for detecting abnormal or suspicious activity in security cameras across a wide array of industries, essentially transforming what were once static, unchanging observers into active participants in decision-making.
Overview of AI Image Recognition

AI image recognition enables machines to identify objects, people, scenes, and actions in images and videos. Using machine learning models trained on large labeled datasets, these systems learn to recognize visual patterns with high accuracy.
Once trained, models can analyze new images and predict their content. Image recognition is widely used in healthcare diagnostics, retail visual search, security monitoring, and social media tagging. As accuracy improves, AI image recognition is becoming a foundational technology in modern digital systems.
How AI Changes the Way Machines Perceive Visuals
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly impacted visual perception in that it allows a machine to learn from data (rather than being based on previously defined rules). This is achieved through deep learning, which allows systems to recognize subtle differences, understand context, and improve continuously.
An example of this is an AI system trained on thousands of images that can distinguish between very similar objects and adapt to variations in lighting or perspective. These features enable advanced applications, including autonomous navigation, emotion recognition, and real-time video analysis.
The Science Behind Computer Vision
Computer vision uses artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and image processing to analyze what a camera or sensor captures visually. The computer can capture data from a camera or sensor and use an algorithm to identify its features and recognize patterns.
The core concepts of computer vision are image classification, object detection, and image segmentation. Image classification assigns a label to an image, object detection identifies the locations of objects in an image, and segmentation identifies the regions of an image for a particular feature. These concepts enable computer vision systems to understand visually.
How Machines Process Images
Image processing begins when cameras convert light into digital signals. These signals are transformed into pixel data, which computers analyze using algorithms.
Machine learning models identify edges, colors, shapes, and textures. Deep learning models, especially neural networks, learn complex visual patterns from large datasets. The processed information is then used in applications ranging from photo management to medical diagnostics and autonomous driving.
Introduction to Visual Data Processing
Data from a camera is processed through several steps to extract usable information about an image or video’s content. These processes, called algorithms, convert unstructured (raw) visual data into a form suitable for decision-making.
Some applications for this field of study are image recognition, video surveillance, medical imaging, virtual reality, and augmented reality. The field of visual data processing draws on principles from computer science and engineering, as well as cognitive science, to develop artificial models of and improve human perception of the environment through vision.
Breakdown of an Image into Pixels
In digital images, each unit (pixel) has a specific color value, and most often this value is represented by three colors: red, green, and blue.
The amount of detail in an image is determined by the number of pixels in that image. The more pixels you have in your image, the higher the resolution will be and therefore the clearer it will look. The opposite is true as well: the fewer pixels in an image, the lower its resolution, and thus the less clear it will look.
Understanding what a pixel is is important for working with images and applying them to fields such as image analysis, photo editing, or computer vision.
Machine Learning in Vision
Through experience-based learning, machine learning enables computer vision systems to become more effective over time. This is done by applying an algorithm to labeled images: the algorithm identifies a pattern in those images and uses it as a model or rule when it encounters new images (data).
These same principles are applied across healthcare, automotive systems, and retail. For example, machine learning can be used in healthcare to analyze medical scan images. Machine learning can also be used in automotive systems to power advanced driver-assistance technologies, such as lane-departure warning systems. In retail, machine learning can enable self-checkout and automated inventory management. While machine learning is very powerful, like all technologies, it relies on high-quality data to produce meaningful results, and careful consideration of how algorithms are trained is necessary to avoid biased and unreliable results.
The Learning Process for Computers
Learning begins by collecting raw data. The clean, labeled data is then divided into two segments for training and testing. Through iterative use of the training data, algorithms learn and are tested against new (unseen) data to evaluate their performance.
As the model iteratively improves its performance through continuous exposure to large amounts of new data, it is ultimately deployed into a real-world application and continues to learn from the new data that it encounters.
Importance of Labeled Data and Algorithms
The basis of all machine learning is labeled data, which trains a model to associate a visual pattern with its label.
The way a model processes labeled data (the algorithm) determines what it can predict.
When high-quality data and effective algorithms are combined, a model can achieve high accuracy in image recognition, object detection, and prediction across various business contexts.
Object Detection Technology
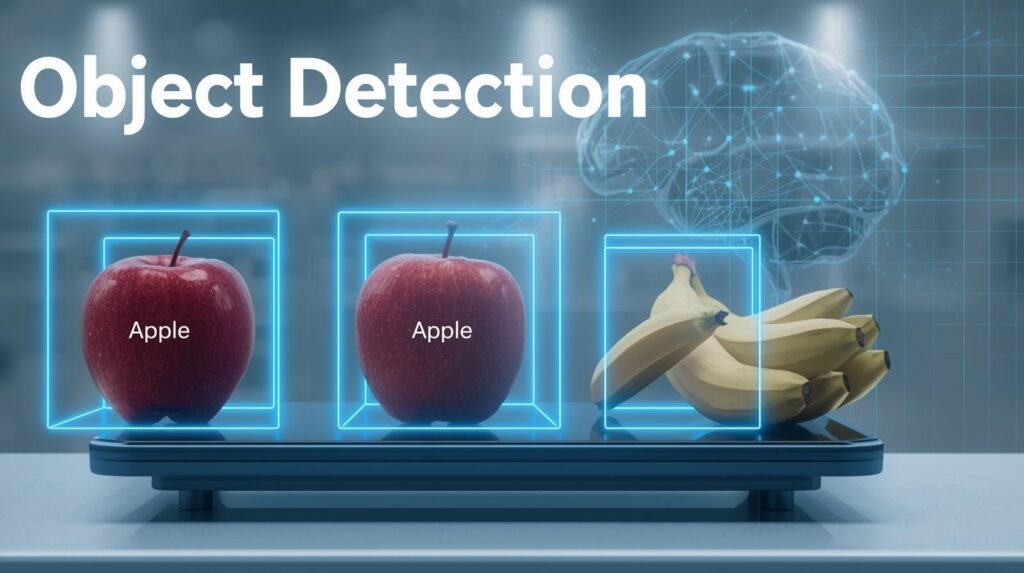
Some key technologies used to achieve this include image processing, machine learning, and deep learning.
Image processing enhances image quality and feature extraction, while machine learning enables pattern identification.
Deep Learning uses neural networks to identify complex patterns in visual data processing.
With these technologies, we can develop many applications, such as facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, robots, diagnostic medicine, and augmented reality.
Difference Between Object Detection and Image Classification
Object Detection identifies one or many subjects of images and their location within the image; Image Classification identifies one (1) object and one (1) subject of an image as the primary item in that image.
Classification asks, “What is in the picture?” Detection asks, “What objects are in this picture? Where are they?”
Both Classification and Detection are essential components of Computer Vision applications.
Use Cases and Examples in Daily Life
Examples of how Computer Vision is used in our everyday lives include: using your smartphone to recognize you (facial recognition), using a traffic monitoring system (detection), using a device to track your fitness activities (classification), and using banking automation for money exchange and other banking activities (classification/detection). The examples above illustrate how Computer Vision can enhance efficiency, safety, and convenience across all aspects of our lives.
Deep Learning Algorithms

Deep learning uses multilayered neural networks to analyze complicated data. Deep learning algorithms will automatically identify important elements from their training datasets, making them excellent tools for applications that require image or voice recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and self-driving vehicles and other autonomous systems.
The increased availability of data and computing resources has enabled researchers and developers to continue making significant advancements in Artificial Intelligence through deep learning.
Overview of Deep Learning Algorithms and Their Significance
Deep learning models are structured like the human brain, using neural networks to process large amounts of data and discover hidden relationships.
It is an extremely significant form of artificial intelligence because of the high degree of accuracy it achieves across many areas, including but not limited to healthcare, financial services, transportation, and digital service providers, and therefore is a fundamental component of modern AI systems.
How Deep Learning Enhances Computer Vision Capabilities
Improving Accuracy and Robustness with Deep Learning: Deep learning enhances the accuracy, robustness, and flexibility of computer vision models. Through deep learning, the model can develop its own feature detectors, handle complex situations, and apply knowledge learned in one environment to another that may be completely different.
Through this process, many areas have achieved great success by applying deep learning to computer vision. These include, but are not limited to:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Facial recognition
- Medical Imaging (Diagnosis)
- Robotics
As these applications grow, so does their need for computer vision to help them understand what they are seeing.
Applications of Computer Vision
In addition to being widely applied across a variety of industries, computer vision is also being applied as a tool in a variety of applications, including:
- Healthcare Diagnostics
- Retail Automation
- Agricultural Monitoring
- Security Surveillance
- Entertainment
The ability of computer vision to solve a wide range of problems and to scale easily makes it an important technological component of automation and intelligent decision-making systems.
Real-World Use Cases
Practical applications illustrate real advantages (faster medical diagnoses, safer transportation, better customer service, and efficient resource management). The examples above illustrate a direct benefit of using computer vision technology.
Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology identifies or verifies individuals by mapping their unique facial characteristics. Facial recognition technology is used in various security systems, Smartphones, Social Media, and Attendance Tracking.
While facial recognition technology has its advantages, there are also privacy and ethics issues that need to be addressed through Regulation and Responsible Use.
Self-Driving Cars and Their Visual Systems
Computer Vision is utilized by Autonomous Vehicles (AV) for perceiving their surroundings via a variety of means including but not limited to Cameras, Radar and LiDAR; utilizing Computer Vision (CV), the AV’s AI model interprets the images captured from cameras and/or other sensors and identifies road lanes, traffic signs, pedestrians and other objects/obstacles that may be present or moving within the field of view of the AV.
Through continuous improvement and learning, CV will provide increasingly safe and efficient modes of transportation.
Future of Computer Vision
Computer Vision has the potential to become even more intelligent, to analyze and process information in real time, and to integrate across an increasing number of industries and applications, such as Healthcare Diagnostics, Autonomous Transportation, and Interactive Technologies.
As Computer Vision continues to be integrated into our daily lives and becomes an integral part of many types of devices, we can expect it to significantly alter how we interact with technology.
Trends and Upcoming Advancements
The future of visual intelligence includes developing new technologies that leverage real-time video analytics, edge-based artificial intelligence (AI), multimodal machine learning, and improved ethical governance systems, all of which will help drive the responsible, more effective use of visual intelligence.
Potential Ethical Concerns and Considerations
Ethical concerns in visual intelligence include privacy, fairness, consent, and accountability. It is necessary to have transparent models of video intelligence, comprehensive and enforceable regulations, and inclusion in decision-making frameworks to create an environment of trust and fairness.
Conclusion
Recap of Computer Vision’s Impact
The influence of computer vision is evident across many industries, as it enables computers to interpret images, making it useful in applications ranging from healthcare diagnosis to self-driving cars and retail automation.
The Importance of Understanding This Evolving Technology
An awareness of computer vision will be important as we are increasingly surrounded by visual data processing and intelligent systems. This awareness will help individuals and companies adapt to and develop new uses for this powerful tool, enabling them to build their future success.